Marine Landforms or Coastal Landforms
- Erosional Landforms: Chasms, Wave-Cut Platform, Sea Cliff, Sea Caves, Sea Arches, Stacks/Skarries/Chimney Rock, Blow Holes or Spouting Horns etc..
- Depositional Landforms: Beach, Bar, Barrier, Spit and Hook, Tombolos etc..
- Coastlines: Coastline of Emergence, Coastline of Submergence, Neutral coastline, Compound coastline and Fault coastline
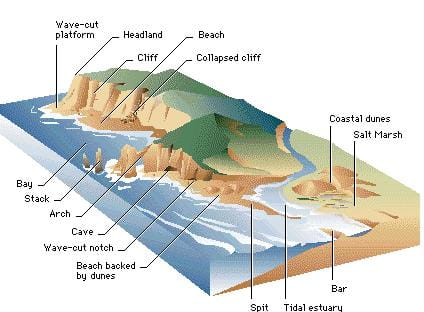
Marine Erosional Landforms
Chasms
- These are narrow, deep indentations (a deep recess or notch on the edge or surface of something) carved due to headward erosion (downcutting) through vertical planes of weakness in the rocks by wave action.
- With time, further headward erosion is hindered by lateral erosion of chasm mouth, which itself keeps widening till a bay is formed.
Wave-Cut Platform
- When the sea waves strike against a cliff, the cliff gets eroded (lateral erosion) gradually and retreats.
- The waves level out the shore region to carve out a horizontal plane or a wave-cut platform.
- The bottom of the cliff suffers the maximum intensive erosion by waves and, as a result, a notch appears at this position.
Sea Cliff
- Shoreline marked by a steep bank (escarpment, scarp).
Sea Caves
- Differential erosion by sea waves through a rock with varying resistance across its structure produces arched caves in rocks called sea caves.
Sea Arches
- When waves from opposite directions strike a narrow wall of rock, differential erosion of the rock leaves a bridge like structure called Sea arch.
Stacks/Skarries/Chimney Rock
- When a portion of the sea arch collapses, the remaining column-like structure is called a stack, skarry or chimney rock.
Hanging Valleys
- If the fluvial erosion of a stream at the shore doesn’t match the retreat of the sea, the rivers appear to be hanging over the sea. These river valleys are called hanging valleys.
Blow Holes or Spouting Horns
- The burst of water through a small hole on a sea cave due to the compression of air in the cave by strong waves. They make a peculiar noise.
Plane of Marine Erosion/Peneplain
- The eroded plain left behind by marine action is called a plain of marine erosion. If the level difference between this plain and the sea level is not much, the agents of weathering convert it into a peneplain.
Marine Depositional Landforms
Beach
- This is the temporary covering of rock debris on or along a wave-cut platform.
Bar
- Currents and tidal currents deposit rock debris and sand along the coast at a distance from the shoreline.
- The resultant landforms which remain submerged are called bars.
- The enclosed water body so created is called a
Barrier
- It is the overwater counterpart of a bar.
Spit and Hook
- A spit is a projected deposition joined at one end to the headland, with the other end free in the sea.
- The mode of formation is similar to a bar or barrier.
- A shorter spit with one end curved towards the land is called a
Tombolos
- Sometimes, islands are connected to each other by a bar called tombolo.
Coastlines
- The boundary between the coast (the part of the land adjoining or near the sea) and the shore (the land along the edge of a sea) is known as the coastline.
Coastlines can be divided into the following classes:
- Coastline of Emergence
- Coastline of Submergence
- Neutral coastline
- Compound coastline
- Fault coastline
- Coastlines are modified either due to the rise or fall in sea levels or upliftment or subsidence of land, or both.
Coastlines of Emergence
- These are formed either by an uplift of the land or by the lowering of the sea level.
- Bars, spits, lagoons, salt marshes, beaches, sea cliffs and arches are the typical features.
- The east coast of India, especially its south-eastern part (Tamil Nadu coast), appears to be a coast of emergence.
- The west coast of India, on the other hand, is both emergent and submergent. The northern portion of the coast is submerged as a result of faulting and the southern portion, that is the Kerala coast, is an example of an emergent coast.
- Coramandal coast == Tamil Nadu Coast == Coastline of emergence
- Malabar coast == Kerala Coast == Coastline of emergence
- Konkan coast == Maharashtra and Goa Coast == Coastline of submergence.
Coastlines of Submergence
- A submerged coast is produced either by subsidence of land or by a rise in sea level.
- Ria, fjord, Dalmatian and drowned lowlands are its typical features.
Ria
- When a region is dissected by streams into a system of valleys and divides, submergence produces a highly irregular shoreline called ria coastline.
- The coast of south-west Ireland is a typical example of ria coastline.
Fjord
- Some coastal regions have been heavily eroded by glacial action and the valley glacier troughs have been excavated below sea level.
- After the glaciers have disappeared, a fjord coastline emerges.
- These coasts have long and narrow inlets with very steep sides.
- The fjord coasts of Norway are a typical example.
Dalmatian
- The Dalmatian coasts result from the submergence of mountain ridges with alternating crests and troughs which run parallel to the sea coast.
- The Dalmatian coast of Yugoslavia is a typical example.
Drowned lowland
- A drowned lowland coast is low and free from indentations, as it is formed by the submergence of a low-lying area.
- It is characterized by a series of bars running parallel to the coast, enclosing lagoons.
- The Baltic coast of eastern Germany is an example of this type of coastline.
Neutral Coastlines
- These are coastlines formed as a result of new materials being built out into the water.
- The word ‘neutral’ implies that there need be no relative change between the level of sea and the coastal region of the continent.
- Neutral coastlines include the alluvial fan shaped coastline, delta coastline, volcano coastline and the coral reef coastline.
Compound Coastlines
- Such coastlines show the forms of two of the previous classes combined, for example, submergence followed by emergence or vice versa.
- The coastlines of Norway and Sweden are examples of compound coastlines.
Fault Coastlines
- Such coastlines are unusual features and result from the submergence of a downthrown block along a fault, such that the uplifted block has its steep side (or the faultline) standing against the sea forming a fault coastline.