Endogenic Forces
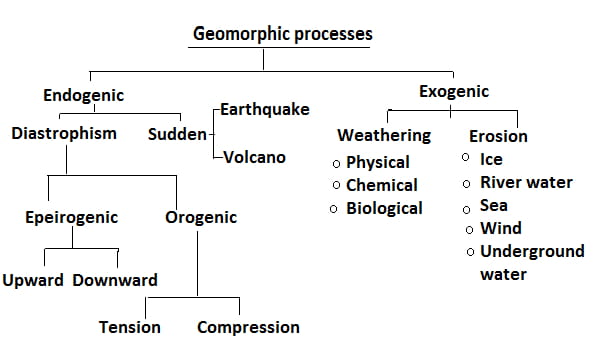
Endogenic forces a can be classified as slow movements (diastrophic) and sudden movements. Slow movements cause changes very gradually which might not be visible during a human lifetime.
Exogenic Forces
The forces which derive their strength from the earth’s exterior or originate within the earth’s atmosphere are called as exogenic forces or external forces.
The action of exogenic forces results in wearing down and hence they are considered as land wearing forces.
Types of Endogenic Forces
Diastrophism or slow-moving force
- All processes that move part of the Earth’s crust up and down come under diastrophism. Diastrophism creates landforms like mountains, continents, oceans, etc.
- The horizontal movement of continents in plate tectonics involves diastrophism forces.
There are two types of diastrophism:
- Orogenic process
- Epeirogenic process
Orogenetic Process
- This force is also called the mountain-building force. On the basis of the direction of force, it can be divided into two parts.
- Tension Force: Due to the diverging force, it caused cracks and faults on the surface of the earth.
- Compression Force: Due to the convergent nature of the force, it causes folding in the earth’s crust.
Epeirogenic process
- Continentals and oceans are formed by the Epeirogenic process because it used to cover a large part of the earth’s crust.
Sudden force
Energy keeps accumulating inside the earth, when this energy suddenly emerges on the surface of the earth, then it is called sudden force. Example
- Earthquake
- Volcano
Types of Exogenic Forces
- Gravitational force
- weathering
- Erosional
- Depositional
Difference between Endogenic and Exogenic Forces
Both endogenic and exogenic forces are equally important because they are the reason behind the earth’s various landforms, such as hills, mountains, volcanos, and more. These two geomorphic pressures give shape to the earth’s surface by formation as well as deformation.
The following table contains the difference between endogenic and exogenic forces, which will help the aspirants to build a link between both processes.
| Endogenic Forces | Exogenic Forces |
| These are internal forces found in the core of the earth. | These external forces are caused by natural elements such as wind, water, and waves. |
| The sole creator of endogenic forces is the interior heat of the earth. | The reason behind exogenic forces is exogenic processes that include weathering, mass wasting, erosion, and so on. |
| These are referred to as constructive forces as they help form the earth’s surface. | These are considered destructive forces because they are very likely to destroy the existing landforms of the earth through erosion, weathering, and other ways. |
| The after-effects of such forces are visible shortly because they cause immediate damage. | The after-effects are visible after thousands and millions of years. |
| Examples: Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain formation. | Examples: Winds, rivers, glaciers, erosion, moon’s tidal force, etc. |