RBI (Reserve Bank of India) is the central bank of India and a statutory body responsible for multiple tasks like printing the currency notes and acting as a custodian to other primary banks of the nation. The RBI was formed on the recommendation of the Hilton-Yong-Commission or commonly referred to as the Royal Commission on Indian currency and finance in April 1934.
The main motive behind setting up RBI was to separate the currency control from the government and provide other banking facilities. The working of RBI is regulated by the RBI governor appointed by the central government of India and the Governor acts as the main decision-maker in RBI.
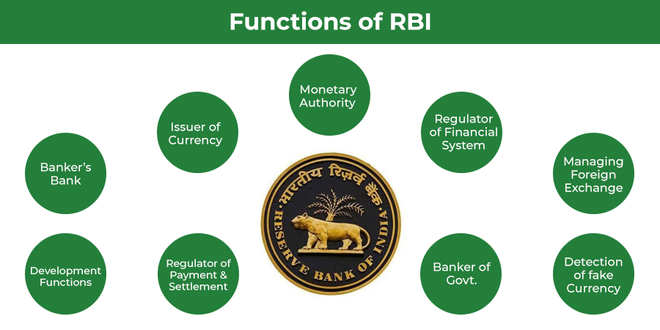
What are the Main Functions of RBI?
- Issue Currency Notes: The issue and printing of currency notes are one of the primary functions of the RBI. The Reserve Bank of India prints notes of all denominations except 1 rupee and that’s because the one rupee note is issued by the Indian Ministry of Finance. The issue and printing of currency notes in India are regulated under the Minimum Reserve System (MRS). As per the MRS, the RBI keeps a reserve asset of Rs 200 crore out of which INR 120 crore would be in form of Gold and the rest in the form of foreign currency. Also, the addition of any new denomination or discontinuation of any existing denomination is being done by RBI. For example, during demonization, RBI discounted old 500 rupee notes and added new 2000 and 500 rupee notes.
- Acting as a Central Bank for other Banks: The Reserve Bank of India acts as a parent bank to all the primary banks operating in India. However hereby RBI plays a role lender that lends money to the primary banks of India on certain interests. Also, it keeps an eye on the financial transactions of the banks so that amount of account holders remains secured in the banks.
- Keeping a Track of Foreign Exchange: Buying and selling foreign currencies and thus making sure a stable foreign exchange in India comes into RBI’s account. RBI holds the right to buy and sell foreign currencies in the international foreign exchange market. Also, RBI makes sure that turbulence in the foreign exchange market does not affect the economy of the nation.
- Acting as a Bank to the Government: The RBI acts as a banker to the central and the state governments of India and fulfils all the banking necessities of the government. Also, RBI plays a crucial role as an advisor to the central government of India and assists the government in framing economic policies for the nation.
- Controlling Credit Flow: The credit made by the primary commercial banks of India is controlled by the RBI. Also, RBI is responsible for regulating the flow of money in the market. RBI adopts both quantitative and qualitative methods to regulate the cash flow in the market. RBI increases or decreases the repo rate to control inflation and regulate the cash flow in the market.
- Other Important Functions: The RBI acts as a representative of India in the IMF (International Monetary Fund), and also in many other major international financial organizations. The RBI is also responsible for looking after government treasures, available securities, foreign reserves, etc. The RBI also plays a major role in the development program run by the central government of India and finances some of these programs. Also, other activities like presenting the economic data of the nation, GDP growth, and the inflation rate is also done by the RBI.
RBI and the Economy of India
After the Central Government of India and the Ministry of Finance, its RBI plays the most crucial role in driving the economy of India. RBI extends its services to the other commercial banks of India and thus these banks provide banking services to the netizens. Also, RBI provides a safe and secure banking infrastructure to people living in India. The RBI tries to keep the repo rate as low as possible to ensure the proper cash flow in the market so that people invest more money in development works. RBI jointly with the central government of India provides ease in foreign trade so that it attracts more FDI (Foreign Direct Investment).


